Does trigger point therapy hurt

There are various forms of trigger point therapy. Some manual therapies such as ischemic compression and pressure release can be painful, while others therapies such as the use of laser and vibration massage treat trigger points a different way, so need not hurt.
In this article we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each, then give the best treatment and strategy to eliminate your trigger points.
CONTENTS
Why some trigger point therapies cause pain and some don't
What is a trigger point
Do you want to temporarily relieve pain, or to eliminate trigger points?
Which trigger point therapy should you use
Getting started
Professionals
Appendix: what the research says about individual therapies
Appendix: trigger points cause pain even when not referring pain
References
Why some trigger point therapies cause pain, and some don't
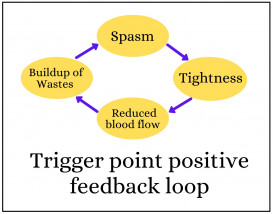
The section below or to the right shows that a trigger point is caused by part of the muscle being in spasm locked on by a feedback loop. Whether a therapy causes pain or not depends on how it attempts to disrupt that loop.
The painful mechanism
Simply speaking the trigger point therapies that hurt attempt to disrupt this feedback loop by applying painful pressure until the pain/spasm mechanism is exhausted. This temporarily allows the muscle to relax and fresh blood to flush the area.
The painless alternatives.
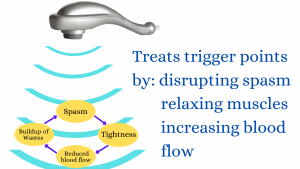
On the other hand those trigger point therapies that don’t cause pain disrupt the feedback loop by addressing one or more parts of that loop. For example, as we will discuss later the vibrations from a vibration massager has the multiple effects of:
- neurologically disrupting the spasm,
- relaxing the muscle to reduce tightness, and
- increasing blood flow which helps flush the toxic wastes.
What is a trigger point
A trigger point is a part of the muscle that has gone into spasm or cramp. As the diagram below shows this spasm is locked on by a feedback loop. Simply, the spasm causes the muscle to tighten putting pressure on the blood vessels restricting blood flow. The restricted blood flow deprives the muscle of oxygen and causes a build up of wastes, making the area around the trigger point toxic. The toxicity causes the muscle to further spasm. This is why trigger points tend to slowly develop over time, and why treatments cause them to settle down, but they build up steam again.
Do you want temporary relief of pain, or to eliminate your trigger points?
Most therapies are applied for the temporary relief of pain rather than to eliminate the trigger point. This is why the pain usually returns. To understand this it is important to look at how trigger points form and what trigger point therapies typically do.
How trigger points form
As this diagram shows trigger points start as a small lump you do not know it is there unless a therapist presses opon it. This lump can gradually grow, and become quite large causing a lot of problems, but still not be referring pain. Eventually the trigger point may be aggravated and start referring pain, and when they do they are arguably the greatest cause of pain syndromes such as back, neck and shoulder pain.

What does trigger point therapies do
According to the reviews of clinical trials of trigger point therapies (1–3) the goal of these therapies is to do as the large blue arrow in the diagram shows: that is to reduce pain and improve function but not eliminate the problem. Scientists call this “deactivation”. In practice it means to revert the trigger point back to how it was before it flared up. You are only aware of the trigger point when a therapist presses upon it, so you feel OK, but of course you're not.

Trigger points are definately still there after your treatment
A few treatments of trigger point therapy may give relief, but the trigger points will definately still be there, and as we discuss in the appendix below even when not causing pain they still cause a lot of problems. A trial performed by the top PhD researchers on trigger points (so the therapies they used were excellent), used 12 very thorough weekly sessions to try and eliminate trigger points (4). The results are shown in this chart. To interpret it please let me introduce two scientific terms:
- Active trigger points: trigger points that hurt without being pressed upon
- Latent trigger points: trigger points that only hurt when pressed upon
From the chart it can be seen that there less active trigger points, hence less pain, but the total number of trigger points has only diminished slightly.

Which trigger point therapy should you use
If you are after trigger point therapy to temporarily relieve pain we've summarised the research findings plus advantages and disadvantages of the common therapies in the appendix below. However, if you are interested in eliminating your trigger points continue and we'll discuss the strategy of how this is done, plus the only therapy that is practically suited to doing this. We will first start with what science tells us about the problem, then how this points to the solution.
Trials show trigger points can be slowly eliminated
The trial of 12 treatments discussed above (4) did manage to diminish trigger points and eliminate some. Two other trials produced similar results. This tells us that if treatment was continued this would further diminish and eliminate trigger points. The main issue though this would require very large numbers of applications of therapy, so at least some of the therapy would need to be self administered, or it would become horrendously expensive.
Finding a suitable trigger point therapy
Identifying the problem
As discussed above trigger points are caused by conditions forming a feedback loop that keeps going around in circles. This is why trigger points slowly develop, and why treatment can diminish them, but they slowly build up steam again (11–14).

Finding a solution
Armed with that knowledge, we need a therapy that that addresses these issues. The ideal solution is vibration massage. Vibrations have been scientifically proven to disrupt spasm, relax muscles and increase blood flow (replenishing oxygen and flushing wastes). We’ve been successfully using vibration massage to treat trigger points in clinic for years. One just sits the vibration massager on the muscle over the trigger point and the trigger point slowly “dissolves”. Better still, with the appropriate advice and massager vibration massage can be easily self applied. For more detail on the effects of vibration please see our article The scientifically proven effects of vibration massage with clinical applications.
Part of a more complex musculoskeletal problem
The last piece of information we need for our elimination strategy is that trigger points are usually part of a more complex musculoskeletal problem, and there are usually things that cause or aggravate them that need to be identified and addressed. Because of this therapy alone is usually not enough. The safe and effective way to eliminate trigger points is to have a professional manage the overall issues and advise you on aspects of self therapy such as where you need to apply it. By having your own vibration massager and following your professional’s advice you can supplement their care with practically unlimited therapy at home.
Getting started
From these three key elements of a successful trigger point elimination strategy you will need to find a professional who deals with trigger points to help manage the overall condition, and in order to get the huge number of application of therapy needed supplement the professional care with self administered vibration massager, following the advice of your professional. To do this you will need a good professional and a good massager.
Finding a professional
If you follow the get a massager link on our website you will find lists of clinics that use and recommend our massagers. If one of them was close by they may be a good place to start. Otherwise, find an appropriately qualified professional such a Chiropractor, Osteopath or Physiotherapist. Be aware though that most will follow the aforementioned scientist’s advice so you may need to discuss this strategy with them.
Using a vibration massager
How to use vibration massage
Using vibration massage is extra-ordinarily easy. We ask you to check our our instructions for the fine points and precautions, but basically all you need to do is place the vibration massager on the muscle over the trigger point and let the vibrations penetrate for 30-60 seconds. This can easily be repeated every day.
How to choose a massager
For how to choose an quality massager that will do a great job and that you will be extremely happy with please see our article How to choose a massager, or you can go straight and check out our economical, easy to use professional standard machines: the General Purpose Massager or our Ultimate Quad Head Massager.

Professionals
DrGraeme massagers were originally built by Dr Graeme for use in his clinic, and to prescribe to his patients for additional self use at home. Now these are used by colleagues and other professionals for similar purposes. If you are a professional and wish to know more about this therapy, or possibly get a sample massager to trial please check out our practitioner page.
Appendix: what the research says about individual trigger point therapies
Below is a summary of the findings of several scientific reviews of trigger point therapies (2,3,5–9).
The goal of trigger point therapy
As said previously, the goal of trigger point therapy, according to the scientists, is to deactivate the trigger points. None mention having the goal of eliminating trigger points.

Dry needling
Most trials show that dry needling provides some short term pain relief and improved function. The risks and potential to cause pain are obvious. The mode of how needles work is still speculation. Where dry needling had been compared with laser the laser has given slightly better results.
Laser
Trial results for laser have been marginally better than those for dry needling, but still only temporary relief. Scientists attribute it’s effect to increasing micro-circulation, improving oxygenation and helping remove waste products. However, this is something that can easily be achieved, if not better, by any competent massage therapist.
Major concern
The big concern with laser is the sheer number of applications of therapy sessions needed for only temporary benefits. For example one trial (10) used 10 daily applications of laser on patients with upper back and neck pain to get a reduction in pain and tenderness for three weeks. Further, according to one review (1) applications of laser should be given from 2-3 times a week though to 5 times a week, with a total of 30 applications of therapy for long term cases. Keep in mind this is just to achieve deactivation, not to eliminate the problem. Assuming each laser consultation costs $50 and takes an hour out of your day that’s $1,500 and 30 hours of your life just for some temporary pain relief, leaving you to front up again next time the problem is aggravated.
Manual therapies
There are various types of manual therapies that involve pressure, massage and stretching of muscles. The trial results for them tend to be similar to those of laser and dry needling. However, according to one review (2) one study did show residual benefit after six months.
What is trigger point release
Trigger point release is a term used to describe relaxing a muscle containing a trigger point and relieving the pain. These are the goals of trigger point therapy, so the terms trigger point release and trigger point therapy tend to be used interchangeably.
Appendix: trigger points cause problems even when not referring pain
As stated, according to the scientists the goal of these therapies is to return the trigger points to a state where they are not referring pain. The obvious issue is potential re-aggravation and more pain, but even without referring pain trigger points cause the following problems. These are discussed in our article Trigger point basics.
- restrict ranges of motion
- cause muscle weakness
- cause muscle fatigue
- alter muscle activations (affecting neurological control of your movements)
- induce muscle cramps, and
- affect posture and joint function, creating further issues.
On top of that, scientists are now finding that latent trigger points still produce sub-threshold levels of pain that over time sensitises the nervous system. This is a major cause of issues such as fibromyalgia and migraines (11)
References
- Uemoto L, Nascimento De Azevedo R, Almeida Alfaya T, Nunes Jardim Reis R, Depes De Gouvêa CV, Cavalcanti Garcia MA. Myofascial trigger point therapy: Laser therapy and dry needling. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17(9).
- Denneny, Diarmuid et al. Trigger point manual therapy for the treatment of chronic noncancer pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;100(3):562–77.
- De Las Peñas CF, Sohrbeck Campo M, Fernández Carnero J, Miangolarra Page JC. Manual therapies in myofascial trigger point treatment: A systematic review. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2005;9(1):27–34.
- Bron C, De Gast A, Dommerholt J, Stegenga B, Wensing M, Oostendorp RAB. Treatment of myofascial trigger points in patients with chronic shoulder pain: A randomized, controlled trial. BMC Med. 2011;9.
- Boyles R, Fowler R, Ramsey D, Burrows E. Effectiveness of trigger point dry needling for multiple body regions: A systematic review. J Man Manip Ther [Internet]. 2015;23(5):276–92. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1179/2042618615Y.0000000014
- Tough EA, White AR, Cummings TM, Richards SH, Campbell JL. Acupuncture and dry needling in the management of myofascial trigger point pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Pain [Internet]. 2009;13(1):3–10. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2008.02.006
- Cagnie B, Castelein B, Pollie F, Steelant L, Verhoeyen H, Cools A. Evidence for the use of ischemic compression and dry needling in the management of trigger points of the upper trapezius in Patients with Neck Pain: A Systematic Review. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;94(7):573–83.
- Espejo-Antúnez L, Tejeda JFH, Albornoz-Cabello M, Rodríguez-Mansilla J, de la Cruz-Torres B, Ribeiro F, et al. Dry needling in the management of myofascial trigger points: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Med . 2017;33(December 2018):46–57.
- Rickards LD. The effectiveness of non-invasive treatments for active myofascial trigger point pain : A systematic review of the literature 2006;9:120–36.
- Hakgüder A, Birtane M, Gürcan S, Kokino S, Tura FN. Efficacy of Low Level Laser Therapy in Myofascial Pain Syndrome: An Algometric and Thermographic Evaluation. Lasers Surg Med. 2003;33(5):339–43.
- Shah J et al. Myofascial Trigger Points Then and Now: A Historical and Scientific Perspective. HHS Public Access. 2015;7(7):746–61.
- Jafri MS. Mechanisms of Myofascial Pain. Int Sch Res Not. 2014;2014:1–16.
- Zhuang XQ, Tan SS, Huang QM. Understanding of myofascial trigger points. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(24):4271–7.
- Bron C, Dommerholt JD. Etiology of myofascial trigger points. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2012;16(5):439–44.
We are continually adding more information on research and uses. Subscribe below to have us email them to you "hot off the press".

About Dr Graeme
Several years ago Dr Graeme, a Chiropractor practicing in Victoria, Australia was looking for a serious hand held massager his patients could use at home to get the extra quality massage they needed. The ones he found in the shops and on-line for home use looked nice but were not serious, and... read more
